Introduction
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary concept, promising secured and transparent data transactions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive, easy-to-understand guide for beginners on the basics of blockchain.
What is Blockchain
Blockchain is a decentralized, digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers worldwide. It’s inherently secure and immutable, making it ideal for recording various types of transactions without the need for a central authority.
How Does Blockchain Work
Blockchain operates on a network of computers connected by a peer-to-peer (P2P) network. Each computer, known as a node, has a copy of the entire blockchain. When a transaction occurs, it is broadcasted to the network for validation.
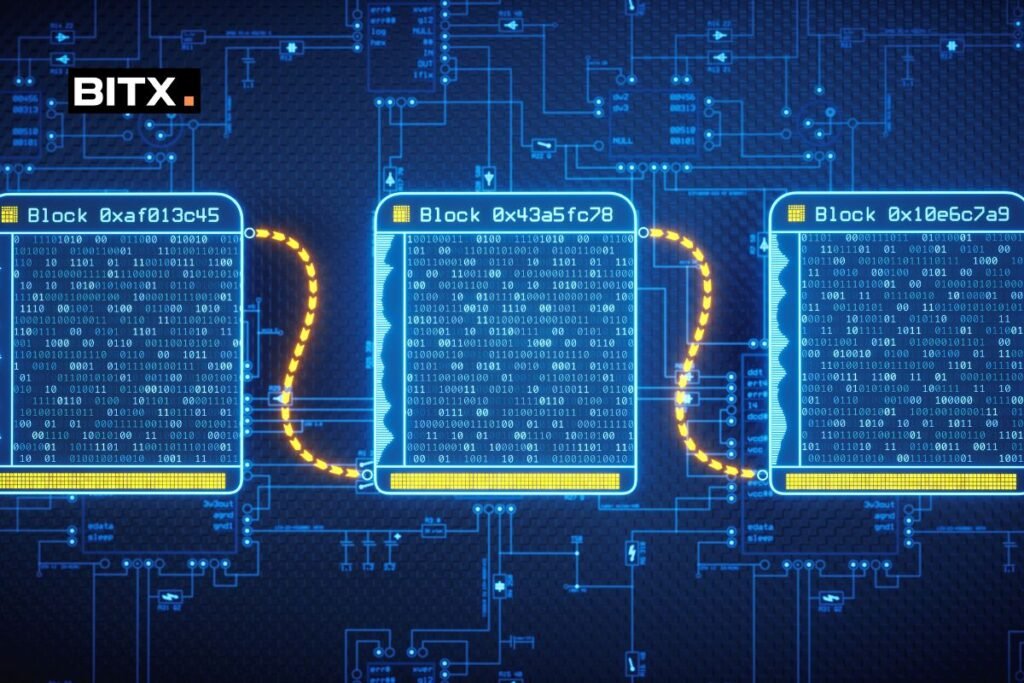
Understanding the Basics: Blocks and Chains
-
Blocks: These are the most basic units of a blockchain. Each block contains a collection of transactions, a timestamp, and a unique code called a hash.
- Chain: A series of blocks, hence the term ‘blockchain.’ Each block contains a reference (hash) to the previous block, creating a chain of blocks linked and secured to each other.
Transactions
A transaction in blockchain is a digital record of assets, data, or information being transferred from one party to another. Transactions are validated through a consensus mechanism called Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake before being added to the blockchain.
Miners and Validation
Miners are individuals or entities that use specialized hardware and software to validate transactions. They compete to solve complex mathematical problems (known as ‘mining’) to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain.
Security and Decentralization
One of the primary advantages of blockchain is its security. Because the blockchain is decentralized and distributed across a network of computers, it is resistant to tampering or hacking. Once a block has been added to the chain, it is virtually impossible to alter it.
Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain has numerous potential applications, including cryptocurrencies, supply chain management, electronic voting, and identity verification. Its transparency, security, and immutability make it an ideal solution for various industries.
Conclusion
While blockchain technology is complex, understanding its basics is key to appreciating its potential applications and impact on modern society. As more businesses and governments explore its use, blockchain promises to reshape various sectors, from finance to healthcare, and beyond.
Further Reading and Resources
For those interested in learning more about blockchain, there are numerous online resources, including articles, videos, and courses available. Some recommended starting points are Bitcoin.org, Blockgeeks, and the online course ‘Blockchain and Bitcoin Fundamentals’ on Coursera.